Meaning of cc in bike:
When it comes to bikes, “cc” is an Short form of ‘cubic centimeters’ using this term to denote the displacement or capacity of the vehicle’s engine. CC in other words is also Cubic capacity. CC in two wheeler explanation
It estimates the displacement of all the cylinders in the engine; the capacity conveys the amount of air fuel mixture that an engine can burn to generate power.
Cc usually translate to power, speed and torque and thus the higher the cc it translates to a bike that can do better in terms of acceleration.
For instance, a 150cc bike has a vehicle engine that has 150 cubic centimetres of the swept volume.
These bikes offer both power and better fuel economy for the regular urban commuters and occasional long-distance riders.
However, higher cc engines also is heavy on fuel as compared to the low cc engines and are also priced higher.
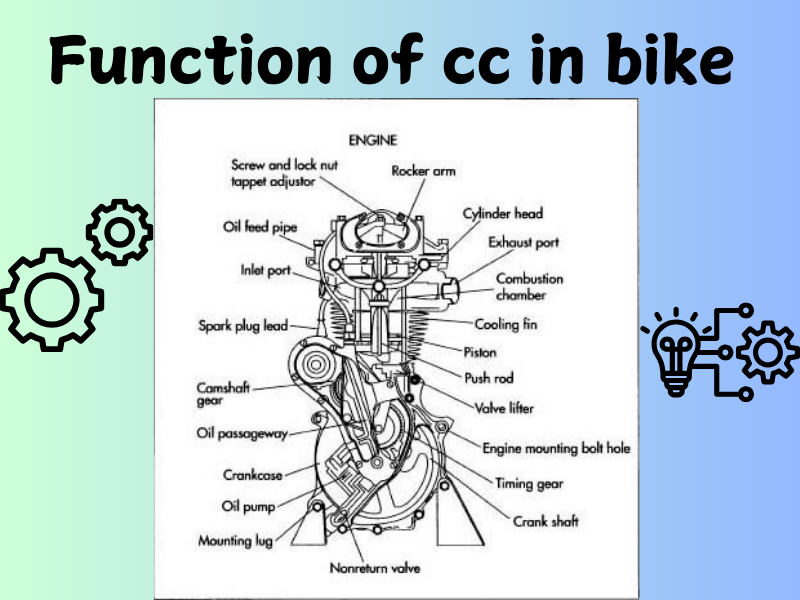
What is the function of cc in bike:
Engine Power and Performance:
Cc engine can mean that a particular bike has more engine capacity for making an efficient combustion of the air and fuel mixture.
That creates more power so that the bike can attain higher speeds, and better acceleration.
Torque Production:
More cc engines develop more torque in terms of strength to help the bike overcome steep gradients, carry load or achieve stability at increased velocity.
Fuel Consumption:
High cc bikes usually have poor fuel economy because more air and fuel has to be burned to produce the power indicated by the cc figure.
As the size of the cc engines is reduced, the fuel efficiency of these power plants increases.
Heat Management:
Large displacement engines produce more heat and therefore a better heat management system is needed for optimum performance of the engines.
How does engine affect the CC performance in bike:
Engine Size and Capacity:
The cc stands for cubic capacities and they represent the whole engine capacity including all the cylinders. Larger engines with high cc have got the volume to contain more air fuel mixture and therefore more explosive combustion.
This means increased horsepower, torque as well as power and general performance.
Power Output:
A higher cc engine produces more power considered on the basis of ability to combust a greater volume of fuel in each cycle.
This equates to better acceleration, increased top speeds and efficiency to work with and transport increased mass or when facing gradient.
Fuel Efficiency:
Most of the time, smaller cc engines are fuel efficient and this is because they do not require large amount of air-fuel mixture to burn.
On the other hand, higher cc engines prefer the power Campisi, (2005) performance over fuel consumption.
Heat and Cooling Requirements:
Cc engines of larger sizes generate more heat as compared to those of the smaller sizes as a result of greater combustion.
This demands more complex cooling structures like liquids to ensure the systems bespoke heat dissipation is enhanced.
Design and Tuning:
They include; Engine size this determines the amount of cc and how it is utilized depends on factors such as compression ratio, valves timing and type of fuel injection system.
Impact of CC in bike:
Power and Performance
Bikes with bigger cc engines are better suited for highways, racing, and off-road experiences,
whereas their smaller counterparts are better suited for city driving.
Fuel Efficiency:
With larger engines, consumption of fuel will go up as performance takes precedence.
Comfort in Riding:
Greater cc engines neck the fuel consumption and result in higher speeds,
while bikes with lower cc engines excel in city driving as they tend to be more lightweight.
Cost and Maintenance:
Lower cc engines are relatively affordable and require less upkeep.
Heat Management:
As cc levels increase air-fuel mixtures will consume more fuel and also produce greater metrics of heat.
How the cc is being calculated in bike:
The abbreviation “cc” on a bike embodiment relates to the Cubic’s engine capacity or cubic centimetre measurement.
It is the sum of all the engines cylinders volume, and it determines the size and ability of the machine.
The higher the value, the more air and fuel the engine is able to burn, thus producing more power.
The cc is calculated through this formula. CC = π×r 2 ×h×n to calculate this there are some variables to be included.
Here: r: is the radius of the cylinder bore, h: is the stroke length, n: is the number of cylinders. In order to consider the cylindrical shape of the cross section of the engine,
this value is usually multiplied by π (approx. 3.1416).
For instance, cylindrical engine type with a bore diameter of 5cm and stroke length measuring 6cm has at least depression volume of single 3.1416 × (2.5) 2 ×6 =117.8 cc1.
This rule holds true for all bike engines.

how to choose correct CC bike while buying a bike:
City Riding:
While choosing a bike with a cc between 100 to 150 it is crucial to consider fuel efficiency and lightweight handling as it will make city commuting convenient.
Touring:
Choosing bikes that fall within the 200 to 400 cc range will ensure highway power and comfort for long rides.
Miscellaneous:
Getting a bike with a cc above 500 would be optimal for someone who is looking for speed and thrill.
but they do come with higher costs alongside maintenance.
Fuel Efficiency:
The amount of fuel consumed per usage by a bike is directly proportional to its cc.
so lower cc bikes such as the previously mentioned 100 to 150 mean less fuel consumption while larger ones will use more.
Experience Level:
It only is proper for a beginner to start off small, with devices that are easy to handle, such as bikes that lay within 150cc.
Owners of bikes above this range, even those who have been riding for a long time, are at a lower risk of crashing.
Budget and Maintenance:
Bikes with a cc of 300 or above tend to be expensive to buy, use, insure, and maintain while lower cc bikes are relatively cheaper.
Hence it is vital to first have a budget in mind.
Legal Requirements:
Always consider the local laws and public systems in place, while buying the Devise are occupation, the appropriate licenses and legal permission set in place are crucial alongside the bike.
Always compare and contrast the bikes available to make an informed decision.
